Or
Option 2
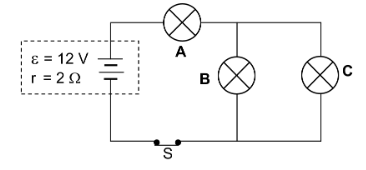
The potential difference across light bulb C is less than the operating voltage. Thus for the same resistance, brightness decreases.
Or
Option 3
In the circuit, the total current in light bulb C is less than the optimum current required (0,5 A). Thus for the same resistance, the power will be less and, therefore, the brightness will decrease.
Or
Option 4
For a given resistance, power is directly proportional to I2. Since the current decreases, brightness decreases.
Or
Option 5
Power is directly proportional/equal to the product of V and I. Since the current decreases, brightness decreases.
Or
The voltage across light bulb C, as well as the current in the bulb, are all less than the optimum values, therefore, the power and brightness are less.